Revolution in Silicon: Intel's Falcon Shores AI Chip Sets New Benchmarks
Image Source: Intel
Intel has taken a significant step by placing orders for its next-generation AI chip, codenamed 'Falcon Shores', with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC). The collaboration utilizes TSMC’s cutting-edge 3nm process node and CoWoS advanced packaging technology. This partnership marks a pivotal shift in Intel’s production strategy, choosing TSMC’s renowned capabilities over its own foundries, a move aimed at tackling NVIDIA’s dominance in the AI chip market.
The Technical Edge of Falcon Shores
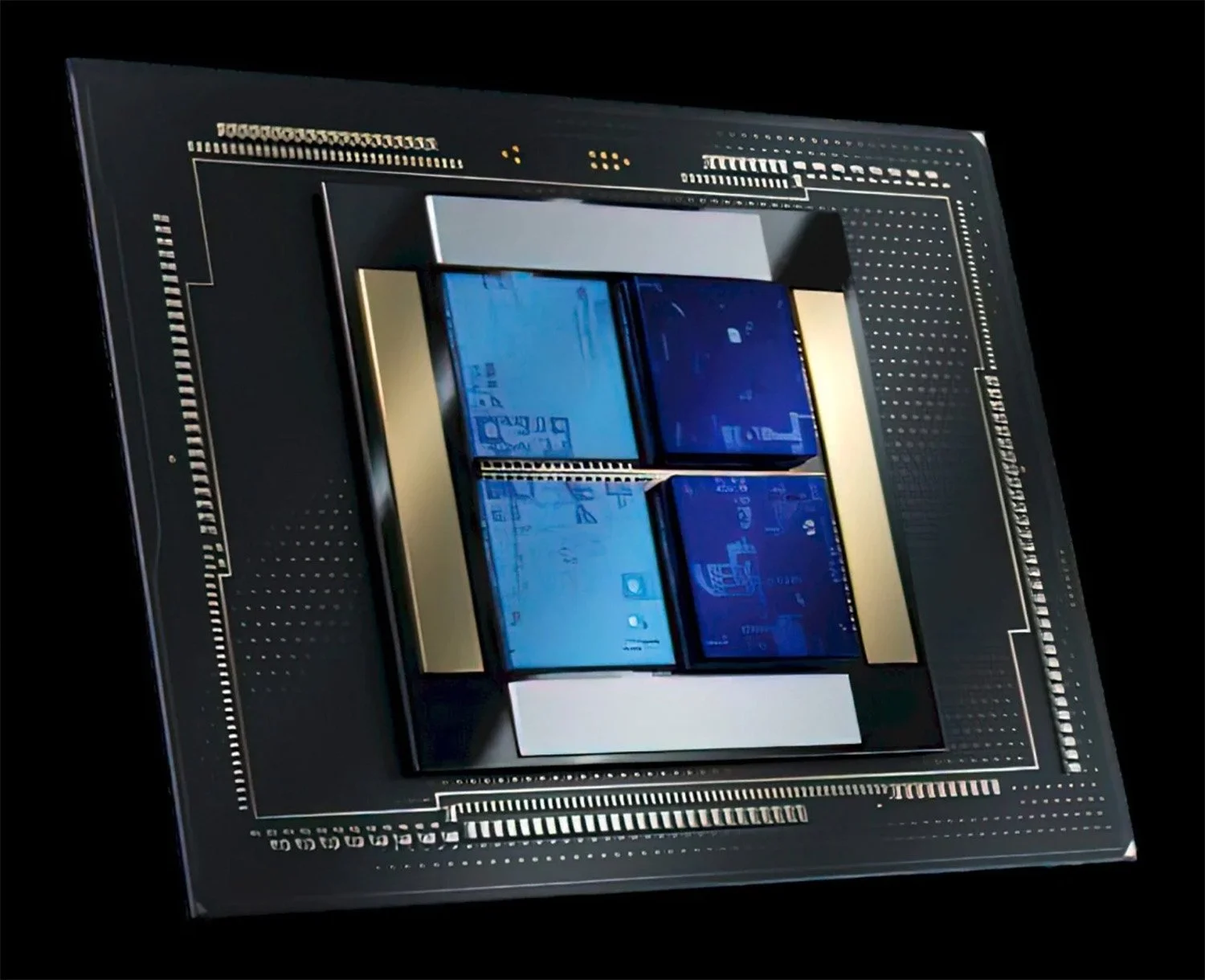
The Falcon Shores AI chip is set to bring a substantial enhancement in performance and efficiency, leveraging the most advanced technologies available. The chip design has completed the tape-out phase and is on track for mass production by late 2025. Intel's decision to integrate Habana's innovative AI technologies with its own robust GPU architecture will significantly amplify its AI computing power, setting a new standard in the industry.
A Platform, Not Just a Product
Intel's vision for Falcon Shores extends beyond a single chip offering. The company is positioning Falcon Shores as a versatile AI chip platform, ensuring backward compatibility with its upcoming Gaudi 3 AI accelerator. This platform strategy includes a broad spectrum of products, spanning high-end to low-end solutions, designed to cater to a diverse range of applications and market needs.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
The use of TSMC's 3nm and 5nm process nodes for Intel's Falcon Shores AI chip exemplifies a major advancement in semiconductor manufacturing. These smaller process nodes allow for a higher density of transistors on a chip, significantly enhancing computational power and energy efficiency. The 3nm technology, in particular, represents one of the most advanced semiconductor technologies available, enabling faster processing speeds and reduced power consumption compared to larger node sizes. Furthermore, the integration of CoWoS-R (Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate with Redistribution layer) advanced packaging technology enhances the chip's ability to handle high-speed signaling and power distribution more efficiently. This packaging method allows for a more compact chip design while improving heat dissipation, which is crucial for maintaining performance at high computation loads. Together, these technologies not only boost the overall performance but also enhance the operational efficiency of the Falcon Shores AI chips, making them well-suited for demanding AI applications that require high throughput and low latency.
Cooling the Power: A Shift in Strategy
The power requirements for next-gen AI chips are enormous, with rumours suggesting that Falcon Shores could consume up to 1500 watts. Intel's approach to cooling these power-hungry chips is reportedly shifting, with plans to move away from exclusively water-cooled solutions. This change reflects broader industry trends towards more sustainable and scalable cooling technologies as the AI arms race heats up.